All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Factors Affecting Sustainability Performance during the Construction Stage in Building Projects-Consultants’ Perspective
Abstract
Background:
The construction industry significantly contributes towards enriching human inhabitation within the built environment. However, the industry generates one-third of the world’s carbon emissions per annum (a major contributor to climate change). In response, a sustainable construction development agenda has been propagated by governments worldwide.
Objective:
This research investigates the factors affecting sustainability performance during the construction stage of building projects in the Gaza Strip from consultants’ viewpoint.
Methods:
A questionnaire was distributed to 35 consultants, and 31 completed questionnaires were returned, representing a response rate of 88.57%. A total of 55 variables were considered in this study and listed within three thematic factor groups, namely, economic, social and environmental factors. Data collected were analysed using factor analysis and relative important index within the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (v22).
Results:
Results indicated that the most influential factors are i) Economic: professional fees of engineers and consultants, energy cost and use of full equipment capacity; ii) Social: availability of knowledge and skills in the labour force, increased burden on infrastructure as a result of the use and depletion of natural resources and public awareness; and iii) Environmental: environmental regulations, pollution generation and waste generation.
Conclusion:
Lack of awareness about economic and social sustainability was found due to the traditional definition of environmental sustainability and the upper and indirect super-vision of consultants to the construction stage.
1. INTRODUCTION
According to the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP, 2012), the building and construction sector directly employs over 111 million people worldwide and significantly contributes to global environmental issues, such as 20% of water use, 25%-40% of energy use, 30%-40% of solid waste generation and 30%-40% of global greenhouse gas emissions. In response, governments worldwide have sought to adopt sustainable construction approaches to mitigate the implications of construction activities on ecology and human health. The main objectives of sustainable construction are to build accessible, secure, healthy and productive buildings while minimising societal, environmental and economic effects [1].
Within the Gaza Strip, the construction industry positively influences the nation’s economic well-being and employs an average of 14.4% of the Palestinian labour workforce (PCU, 2016) [2]. However, the country has historically been subject to external and internal political, economic and social pressures that have led to poor socioeconomic conditions. To further exacerbate this issue, the Gaza Strip lacks natural resources and is consequently highly dependent on donors [3]. Therefore, promoting and applying sustainable construction methods and practices in Gaza Strip can generate new job opportunities in not only occupations similar to those in conventional construction but also entirely new ‘green jobs’ [4].
This research aims to investigate the factors affecting sustainability performance during the construction stage of building development in the Gaza Strip from the consultants’ viewpoint.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1. Sustainable Construction
Kilbert (1994) [5] first acknowledged the need for sustainable construction during the first international conference on sustainable construction that was held in Tampa, Florida, United States of America where sustainable construction was defined as ‘creating and operating a healthy built environment based on resource efficiency and ecological design’ [6]. Since then, others have contributed to the discourse. For example, CIB (1999) concluded that sustainable construction is the minimisation of resource consumption, maximisation of resource reuse, use of renewable and recyclable resources, protection of the natural environment, creation of a healthy and non-toxic environment and pursuit of quality in creating the built environment. Similarly, G. Ofori [7] recognised sustainable construction as ‘creating construction items using best-practice clean and resource-efficient techniques, from the extraction of the raw material to the demolition and disposal of its components.’ From the perspective of a developing country, the Agenda 21 for Sustainable Construction in Developing Countries defined sustainable construction as ‘a holistic process aiming to restore and maintain harmony between the natural and the built environments and create settlements that affirm human dignity and encourage economic equity’ [8].
Airport Cooperative Research Program [9] recognised sustainable construction as ‘practices that have sustainability benefits during the construction stage of a project, including those benefits that may result from decisions made during the planning and design stages of a project.’
O’Connor [10], defined ‘sustainable construction’ as the processes, decisions and actions during the construction stage of capital projects that enhance current and future environmental, social and economic needs whilst considering project safety, quality, cost and schedule.
2.2. Sustainable Construction Pillars
According to the study [11], sustainable development has three essential aspects: i) environmental responsibility, ii) social awareness and iii) economic profitability. Achieving the optimum balance between these factors supports true sustainability (Kibwami & Tutesigensi, 2016). Similarly, sustainable construction embraces three aspects, namely, social, economic and environmental considerations; by contrast, the traditional perspective is concerned with the economy, utility and durability [12, 13]. However, several researchers, such as [6] and [14], added a technical pillar as the fourth issue; the technical pillar includes durable, reliable and functional building structures with the inherent desire to inextricably link quality in all project processes.
2.3. Construction Stage
In social and natural sciences, every element has a life cycle, which represents maturational and generational processes driven by mechanisms of reproduction in the natural population [15]. Ritz [16] suggested that the construction project life cycle encompasses the conceptual stage through project definition, execution, operation and finally, demolition. According to the study [5], the project life cycle is a process of planning, development, design, use, maintenance and deconstruction [17, 18]. However, Shen and Tam [19, 20] decomposed the project life cycle into inception, design, construction, operation and demolition.
Weaver et al. [21] suggested that the construction stage transfers the project design plans into reality. However, O’Connor et al. [10] defined the ‘construction stage’ as all fabrication/jobsite/field activities and decisions, starting with construction/fabrication contracting and planning for site mobilisation continuing to initial operations, final performance testing and handover of the completed facility.
2.4. Factors Affecting Sustainability Performance During the Construction Stage of Project Development
Several factors affect sustainability performance during the construction stage. These factors can be conveniently examined through the three lenses of economic, social and environmental sustainability factors.
3. METHODOLOGY
In this study, a questionnaire survey was conducted to gather the opinions, views and attitudes of the participants. The questionnaire is the most widely applied method for data collection for descriptive and inferential surveys. Furthermore, the questionnaire is a fast and simple technique of data collection and is precise when beginning to explore and analyse the collected data. A total of 55 factors that might affect sustainability performance during the construction stage in building projects were defined through a detailed literature review of relevant research. Twenty-seven previous studies were incorporated into this study to compile a comprehensive list of factors.
The selected factors and their related thematic groups are shown in (Table 1). The factors were tabulated in a questionnaire form, and this data collection instrument was reviewed by three groups of experts to test its content validity. This test led to the introduction of minor amendments (to well suit the local market conditions) prior to distributing the questionnaire to the target research population.
3.1. Sample Size
The target population in this study is all 38 consultants with valid registration in the Association of Engineers (AE, 2017). The following formula in Eq. (1) was used to determine the sample size of unlimited population [47].
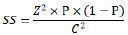 |
(1) |
| IDENTIFIED FACTORS FOR THIS RESEARCH | REFERENCE |
| ECONOMIC SUSTAINABILITY VARIABLES | |
| Water cost | [15, 22, 23] |
| Energy cost | [10, 15] |
| Material costs | [15, 23, 25] |
| Land cost | [22, 23] |
| Labor cost (experienced in sustainable buildings) | [15, 23-25] |
| Professional fees such as engineers and consultants | [15, 23] |
| Cost of using existing equipment | [15] |
| Cost of purchase or renting new equipment | [15] |
| Cost of installation of equipment and tools | [15] |
| Right-sizing of construction equipment | [10] |
| Use of full equipment capacity | [10] |
| Inspection and maintenance of construction equipment | [10] |
| Cost of securing and protecting the site | [15] |
| Durability | [22, 25] |
| Cost of repairing errors and defects | [25, 26] |
| Lead-times for the required tasks and activities | [25, 26] |
| SOCIAL SUSTAINABILITY VARIABLES | |
| Creating jobs due to the need of labors | [6, 25, 27] |
| Reliance on intensive labour rather than intensive equipment | [10] |
| Creating jobs for local employment directly | [10, 15, 28-31] |
| Creating jobs for local employment indirectly | [10, 15, 28-31] |
| Influence of the project on job market | [25] |
| Labor availability | [25] |
| Availability of knowledge and skills in the labour force | [32] |
| Promotion and development of capacity and skills for the labour force | [6, 10, 30, 33, 34] |
| Health and safety at work place | [6, 10, 15, 23, 29, 33, 35-37] |
| Working conditions | [38] |
| Physical space of the building | [25] |
| Aesthetic options of the building | [25, 39] |
| Participation of all parties in project monitoring and decision-making | [34] |
| Project control guidelines | [32] |
| Public awareness | [32] |
| Improvement of infrastructure to the society and environment | [15] |
| Increased burden on infrastructure as a result of the use and depletion of natural resources | [15] |
| ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY VARIABLES | |
| Integrated environmental and economic program | [38, 40] |
| Communication of environmental management information | [15] |
| Environmental management technology | [15, 23] |
| Environmental regulations | [15, 23] |
| Inclusion of environmental aspects in decisions during construction (e.g. buying greener materials) | [6, 10, 23, 29] |
| Institutional interest to the environmental aspect | [15, 41] |
| Ecology preservation | [10, 15, 40] |
| Use of sustainable temporary facilities (such as desks and bathrooms) during the project | [10] |
| Use of sustainable material substitutions | [10] |
| Use of recyclable/renewable materials | [10, 25, 38] |
| Recycling of products | [6, 25, 29, 31, 34, 42, 43] |
| Reuse of products | [6, 10, 15, 25, 29, 31, 34, 43] |
| Management of surplus materials | [10] |
| Waste generation | [15, 25, 44] |
| Waste disposal | [25, 40] |
| Waste management | [10, 23, 45] |
| Depletion of dependency resources (water-energy-raw materials-land) | [6, 10, 15, 23, 25, 29, 43, 44, 46] |
| Site attributes | [38] |
| Pollution generation | [10, 15, 23, 25, 45] |
| Natural habitat destruction | [15, 22] |
| Changes in the environment lead to the discomfort of people and the biological system. | [15, 22] |
| Health and safety risks | [15, 22] |
Where, SS = Sample Size; Z = Z value (e.g. 1.96 for 95% confidence level); p = percentage selecting a choice, expressed as a decimal (0.5 used for sample size needed); and c = confidence interval, expressed as a decimal (e.g. 0.05 = ±5).
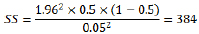 |
Correction for finite population:
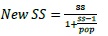 |
Where, New SS = corrected Sample Size.
The sample size for the 38 consultants was calculated as follows:
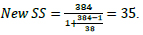 |
Therefore, the calculated sample size is 35 consultants based on a 95% confidence level.
The questionnaires were consequently distributed to 35 consultants asking their contribution in ranking the determined 55 factors by using an ordinal scale. The ordinal scale used was 1 = very low influence, 2 = low influence, 3 = moderate influence, 4 = high influence and 5 = very high influence. A total of 31 completed questionnaires were received from the consultants, representing a good response rate of 88.57%. Tests of validity (internal and structure) and reliability of the questionnaire were conducted. In addition, the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality was used to ascertain the parametric nature of data distribution.
3.2. Analysis
The collected raw data were first sorted, edited, coded and then entered into computer software. Two software were used, the Excel sheet and SPSS. The ordinal scale is a rating data, which uses integers in ascending or descending order. The Relative Important Index (RII) was used in the analysis. Moreover, Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) tests, frequencies and percentiles were used. The RII method has been widely used in construction research for calculating and formulating attitudes with respect to surveyed variables. Then, the RII was computed using the following formula in Eq. (2) [48-51]:
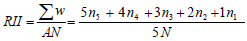 |
(2) |
Where, W is loading given for every factor by the respondent, between 1 to 5, (n1= number of respondents for who agreed strangely, n2 = number of respondents who don't agree, n3 = number of respondents for neutral, n4 = number of respondents for agree, n5 = number of respondents who agreed strangely). A is the first load (i.e. 5 in the study) and N is the total number of samples. RII value is between 0 and 1. The analyzed data was finally presented using descriptive methods for easy interpretation and to enable and to make comparison easy.
4. ANALYSIS OF RESULTS
4.1. Economic Sustainability Factor
Table 2 illustrates that the first run had 16 variables, and the KMO value was 0.469 (should be > 0.50); thus, several weak variables were omitted to meet statistical requirements for sample adequacy. In addition, the Bartlett’s test for sphericity with chi-square = 244.857 at a significance level of p-value = 0.00 (should be < 0.05) meets the requirements. Cronbach’s alpha was 0.70, which was accepted. After the final run, six variables remained, the KMO value was 0.600, and the Bartlett’s test for sphericity (with chi-square = 244.857) at a significance level of p-value < 0.001, hence meeting the requirements. Cronbach’s alpha was 0.739, which was accepted.
Following the tests and using principal component analysis, six variables remained, and 10 variables were deleted because their factor loading values (less than 0.5) were considered very low (Table 3).
| KMO and Bartlett's Test | |||
| Item | Factor Analysis Run Description | ||
| First Run | Final Run | ||
| Number of Included Variables | 16 | 6 | |
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy. | 0.469 | 0.600 | |
| Bartlett's Test of Sphericity | Approx. Chi-Square | 244.857 | 244.857 |
| Df | 120 | 120 | |
| Sig. (P-value) | 0.00 | < 0.001 | |
| Cronbach's alpha | 0.70 | 0.739 | |
| No. | Economic Sustainability Variables | Variable Loadings |
| 1 | Right-sizing of construction equipment | 0.774 |
| 2 | Use of full equipment capacity | 0.658 |
| 3 | Professional fees such as engineers and consultants | 0.649 |
| 4 | Inspection and maintenance of construction equipment | 0.632 |
| 5 | Energy cost | 0.538 |
| 6 | Cost of repairing errors and defects | 0.506 |
| 7 | Labor cost (experienced in sustainable buildings) | Removed |
| 8 | Lead-times for the required tasks and activities | Removed |
| 9 | Cost of securing and protecting the site | Removed |
| 10 | Durability | Removed |
| 11 | Cost of purchase or renting new equipment | Removed |
| 12 | Cost of installation of equipment and tools | Removed |
| 13 | Land cost | Removed |
| 14 | Material costs | Removed |
| 15 | Water cost | Removed |
| 16 | Cost of using existing equipment | Removed |
The mean of the economic sustainability variable equals 3.10 and RII = (62.04%) (Table 4). The mean is close to the neutral, indicating low awareness of the economic sustainability amongst the respondents.
The results clarify that the variable ‘professional fees of engineers and consultants’ was ranked first with mean = 3.29 and RII = (65.81%). These results are consistent with those of the study [23] who reported that this variable is important because it has a managerial focus, that is, engineers and consultants control most other variables affecting sustainability performance during the construction stage of project development. The factor ‘energy cost’ came second with mean = 3.23 and RII = (64.52%). These findings agree with those of [52], who noted that on average, green buildings use 25% less energy and emit 34% less carbon dioxide than commercial buildings. Moreover, this study [53] considered that green buildings conserve energy, land, water and materials. In the third position was the variable ‘use of full equipment capacity’ with a mean = 3.03 and RII = (60.65%). The use of equipment without full capacity can reduce their default life and expose them to depreciation in a short time, increasing cost and consuming new resources, which in turn affects sustainability [10]. Other variables were right-sizing of construction equipment, inspection and maintenance of construction equipment and cost of repairing errors and defects.
4.2. Social Sustainability Factor
Table 5 illustrates that 18 variables were entered into the first run, and the KMO value was 0.499 (should be > 0.50); several weak variables were omitted to meet statistical requirements for sample adequacy. In addition, the Bartlett’s test for sphericity has Chi-square = 352.705 at a significance level of p-value = 0.00 (should be < 0.05), hence meeting the requirements. Cronbach’s alpha was 0.839, which was accepted. After the final run, the 12 variables remained, the KMO value was 0.600 and Bartlett’s test for sphericity with chi-square = 352.705 at a significance level of p-value < 0.001, thereby meeting the requirements. In addition, Cronbach’s alpha was 0.864, which was accepted.
| Economic Sustainability Variables | Mean | RII (%) | Rank |
| Professional fees such as engineers and consultants | 3.29 | 65.81 | 1 |
| Energy cost | 3.23 | 64.52 | 2 |
| Use of full equipment capacity | 3.06 | 61.29 | 3 |
| Right-sizing of construction equipment | 3.03 | 60.65 | 4 |
| Inspection and maintenance of construction equipment | 3.03 | 60.65 | 4 |
| Cost of repairing errors and defects | 2.97 | 59.35 | 6 |
| All items of the field | 3.10 | 62.04 | - |
| KMO and Bartlett's Test | |||
| Item | Factor Analysis Run Description | ||
| First Run | Final Run | ||
| Number of Included Variables | 18 | 12 | |
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy. | 0.499 | 0.600 | |
| Bartlett's Test of Sphericity | Approx. Chi-Square | 352.705 | 352.705 |
| Df | 136 | 136 | |
| Sig. (P-value) | 0.00 | < 0.001 | |
| Cronbach's alpha | 0.839 | 0.864 | |
Following the tests and using principal component analysis, 12 variables remained, and six variables were deleted because their factor loading values were less than 0.5, which was considered very low (Table 6).
The mean of the social sustainability variable = 3.00 and RII = (59.95%) (Table 7). The mean is equal to the neutral level, and most of them are below the neutral. Therefore, respondents are unaware of the social sustainability amongst respondents. This lack of awareness is a result of the traditional definition of environmental sustainability.
| No. | Social Sustainability Factors | Variable Loadings |
| 1 | Aesthetic options of the building | 0.740 |
| 2 | Participation of all parties in project monitoring and decision-making | 0.694 |
| 3 | Physical space of the building | 0.680 |
| 4 | Project control guidelines | 0.675 |
| 5 | Health and safety at workplace | 0.659 |
| 6 | Promotion and development of capacity and skills for the labour force | 0.630 |
| 7 | Creating jobs for local employment indirectly | 0.629 |
| 8 | Increased burden on infrastructure as a result of the use and depletion of natural resources | 0.588 |
| 9 | Public awareness | 0.583 |
| 10 | Working conditions | 0.558 |
| 11 | Availability of knowledge and skills in the labour force | 0.552 |
| 12 | Creating jobs for local employment directly | 0.536 |
| 13 | Influence of the project on the job market | Removed |
| 14 | Labor availability | Removed |
| 15 | Creating jobs due to the need of labors | Removed |
| 16 | Improvement of infrastructure to the society and environment | Removed |
| 17 | Reliance on intensive labour rather than intensive equipment | Removed |
| Social Sustainability Variables | Mean | RII (%) | Rank |
| Availability of knowledge and skills in the labour force | 3.45 | 69.03 | 1 |
| Increased burden on infrastructure as a result of the use and depletion of natural resources | 3.23 | 64.52 | 2 |
| Public awareness | 3.19 | 63.87 | 3 |
| Promotion and development of capacity and skills for the labour force | 3.13 | 62.58 | 4 |
| Working conditions | 3.10 | 61.94 | 5 |
| Physical space of the building | 2.90 | 58.06 | 6 |
| Aesthetic options of the building | 2.90 | 58.06 | 6 |
| Participation of all parties in project monitoring and decision-making | 2.90 | 58.06 | 6 |
| Health and safety at work place | 2.87 | 57.42 | 9 |
| Creating jobs for local employment directly | 2.87 | 57.42 | 9 |
| Creating jobs for local employment indirectly | 2.81 | 56.13 | 11 |
| Project control guidelines | 2.61 | 52.26 | 12 |
| All items of the field | 3.00 | 59.95 | - |
The results illustrate that the variable ‘availability of knowledge and skills in the labour force’ was ranked first with mean = 3.45 and RII = (69.03%). Given that sustainability is a relatively new concept within the Gaza Strip, consultants lack pertinent knowledge and skills, and further effort should be made by industry leaders and the government to educate professionals within the sector (c.f) [32]. The variable ‘increased burden on infrastructure as a result of the use and depletion of natural resources’ was ranked second with mean = 3.23 and RII = (64.52%). Any project developed can invariably increase the demand for supporting infrastructure (i.e. water, road, energy, services and space), thus placing a further burden on achieving sustainable construction practices. In the third position was the variable ‘public awareness’ with mean = 3.19 and RII = (63.87%). This result is consistent with that of [32] who illustrated that increasing public awareness is essential to delivering sustainable practices. Other factors were promotion and development of capacity and skills for the labour force, working conditions, physical space of the building, aesthetic options of the building, participation of all parties in project monitoring and decision making, health and safety in the workplace, directly creating jobs for local employment, indirectly creating jobs for local employment and project control guidelines.
4.3. Environmental Sustainability Factor
Table 8 illustrates that the first run had 22 variables, and the KMO value was 0.605 (should be > 0.50), which meets the statistical requirements for sample adequacy. In addition, the Bartlett’s test for sphericity with chi-square = 431.325 at a significance level of p-value = 0.00 (should be < 0.05), meeting the requirements. Cronbach’s alpha was 0.85, which was accepted. After the final run, 13 variables remained, the KMO value was 0.600 and Bartlett’s test for sphericity with chi-square = 431.325 at a significance level of p-value < 0.001, hence meeting the requirements. Cronbach’s alpha was 0.891, which was accepted.
Following the tests and using principal component analysis, 13 variables remained, and nine variables were deleted because their factor loading values were less than 0.5, which was considered very low (Table 9).
The mean of the ‘environmental sustainability’ variable = 3.14 and RII = (62.88%) (Table 10). Most variables have a mean more than 3, indicating awareness of the environmental sustainability amongst respondents. This value is accepted with the traditional definition of environmental sustainability in developing areas.
| KMO and Bartlett's Test | |||
| Item | Factor Analysis Run Description | ||
| First Run | Final Run | ||
| Number of Included Variables | 22 | 13 | |
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy. | 0.605 | 0.605 | |
| Bartlett's Test of Sphericity | Approx. Chi-Square | 431.325 | 431.325 |
| Df | 231 | 231 | |
| Sig. (P-value) | 0.00 | < 0.001 | |
| Cronbach's alpha | 0.85 | 0.891 | |
| No. | Environmental Sustainability Variables | Variable Loadings |
| 1 | Communication of environmental management information | 0.792 |
| 2 | Ecology preservation | 0.775 |
| 3 | Institutional interest to the environmental aspect | 0.772 |
| 4 | Environmental management technology | 0.757 |
| 5 | Environmental regulations | 0.719 |
| 6 | Recycling of products | 0.715 |
| 7 | Integrated environmental and economic program | 0.701 |
| 8 | Reuse of products | 0.597 |
| 9 | Use of recyclable/renewable materials | 0.578 |
| 10 | Use of sustainable temporary facilities (such as desks and bathrooms) during the project | 0.551 |
| 11 | Waste generation | 0.525 |
| 12 | Changes in the environment lead to the discomfort of people and the biological system | 0.512 |
| 13 | Pollution generation | 0.512 |
| 14 | Inclusion of environmental aspects in decisions during construction (e.g. buying greener materials) | Removed |
| 15 | Management of surplus materials | Removed |
| 16 | Waste disposal | Removed |
| 17 | Depletion of dependency resources (water-energy-raw materials-land) | Removed |
| 18 | Use of sustainable material substitutions | Removed |
| 19 | Natural habitat destruction | Removed |
| 20 | Waste management | Removed |
| 21 | Site attributes | Removed |
| 22 | Health and safety risks | Removed |
| Environmental Sustainability Variables | Mean | RII (%) | Rank |
| Environmental regulations | 3.52 | 70.32 | 1 |
| Pollution generation | 3.42 | 68.39 | 2 |
| Waste generation | 3.32 | 66.45 | 3 |
| Reuse of products | 3.26 | 65.16 | 4 |
| Changes in the environment lead to the discomfort of people and the biological system | 3.23 | 64.52 | 5 |
| Institutional interest to the environmental aspect | 3.16 | 63.23 | 6 |
| Communication of environmental management information | 3.13 | 62.58 | 7 |
| Recycling of products | 3.10 | 61.94 | 8 |
| Use of sustainable temporary facilities (such as desks and bathrooms) during the project | 3.00 | 60.00 | 9 |
| Integrated environmental and economic program | 2.97 | 59.35 | 10 |
| Environmental management technology | 2.94 | 58.71 | 11 |
| Use of recyclable/renewable materials | 2.94 | 58.71 | 11 |
| Ecology preservation | 2.90 | 58.06 | 13 |
| All items of the field | 3.14 | 62.88 | - |
The results exhibit that the variable ‘environmental regulations’ was ranked first with mean = 3.52 and RII = (70.32%). This finding concurs with that of [38] who proposed that environmental regulations support the implementation of a government-backed sustainability agenda, and sustainability cannot be readily achieved without them. This view is recently supported by [23], who expressed that environmental regulations are the most important factors affecting sustainability performance. The factor ‘pollution generation’ came second with mean = 3.42 and RII = (68.39%). The most adverse environmental effect of construction activities is the pollution generated [10, 15, 45], and the sector infamously contributes from 40% to 50% of the world’s greenhouse gas emissions [54]. In the third position was the variable ‘waste generation’ with mean = 3.32 and RII = (66.45%). These results concur with previous findings [25, 41, 44] that waste generation is an important factor that affects sustainability performance during the construction stage. Other factors are reuse of products, changes in the environment leading to the discomfort of people and the biological system, institutional interest on the environmental aspect, communication of environmental management information, recycling of products, use of sustainable temporary facilities (such as desks and bathrooms) during the project, environmental management technology, use of recyclable/renewable materials and ecology preservation.
5. DISCUSSION
A total of 55 factors affecting sustainability performance during the construction stage in the building projects in the Gaza Strip were considered in this study, and 31 remained after factor analysis. The consultants ranked the most influential economic (professional fees of engineers and consultants, energy cost and use of full equipment capacity); social (availability of knowledge and skills in the labour force, increased burden on infrastructure as a result of the use and depletion of natural resources and public awareness); and environmental factors (environmental regulations, pollution generation and waste generation).
However, lack of awareness about economic and social sustainability was observed due to the traditional definition of environmental sustainability and the upper and indirect supervision of consultants to the construction stage.
Making new strategies to encourage sustainable construction, such as granting building permits at half price for green buildings, is recommended. The awareness about sustainability amongst stakeholders in the construction process should be enhanced through lectures and workshops conducted by the Palestinian Contractors Union and the AE.
Sustainability and sustainable practices must be promoted by the Ministry of High Education by adding special units in textbooks for all generations.
CONCLUSION
The main objectives of this study are to identify the factors affecting sustainability performance during the construction stage in the building projects in the Gaza Strip and to determine their level of influence from the consultants’ viewpoint. A total of 55 factors were considered in this study, and 31 remained after factor analysis. These factors are listed under three groups: (1) economic, (2) social and (3) environmental. The consultants ranked the most influential economic factors, such as professional fees of engineers and consultants, energy cost, use of full equipment capacity, right-sizing of construction equipment, inspection and maintenance of construction equipment and cost of repairing errors and defects. The consultants also rated the most influential social factors, namely, availability of knowledge and skills in the labour force, increased burden on infrastructure as a result of the use and depletion of natural resources, public awareness, promotion and development of capacity and skills for the labour force, working conditions, physical space of the building, aesthetic options of the building, participation of all parties in project monitoring and decision making, health and safety at workplace, directly creating jobs for local employment, indirectly creating jobs for local employment and project control guidelines. Furthermore, the consultants ranked the most influential environmental factors, such as environmental regulations, pollution generation, waste generation, reuse of products, changes in the environment lead to the discomfort of people and the biological system, institutional interest to the environmental aspect, communication of environmental management information, recycling of products, use of sustainable temporary facilities (e.g. desks and bathrooms) during the project, environmental management technology, use of recyclable/renewable materials and ecology preservation.
Lack of awareness about economic and social sustainability was found due to the traditional definition of environmental sustainability and the upper and indirect supervision of consultants to the construction stage.
CONSENT OF PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
Not applicable.
FUNDING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Declared none.


