All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Stakeholders’ Insight on the Delay of Constructions Projects in the Makkah Region- KSA
Abstract
Aims:
This study aims to identify the major causes of delays in construction projects in the Makkah region of Saudi Arabia. It investigates the opinions of different stakeholders separately to ensure partiality and objectivity.
Background:
Saudi Arabia's construction industry is experiencing rapid expansion, with no shortage of contracts in any sector, either from housing or utilities to transport infrastructure. Public spending is driving the contracting industry forward [Oxford]. The construction industry contributed between 30% to 40% of the non-oil productive sectors at the end of each National Development Plan from 1980 to 2000. Makkah receives around two million pilgrims during the annual Hajj and more than 20 million visitors for performing Umrah (Al-Emad). Substantial public funds have been spent on construction projects to develop Makkah during recent years. Real estate, infrastructure, hospitals, and retail sectors are among those most likely to benefit. Most of these projects suffered delays and their consequences. The Saudi Ministry of Municipal and Rural Affairs (MOMRA) and the Ministry of Transportation acknowledged public construction project delays. They reported that approximately 75% of them exceeded their scheduled time. This is one of the main reasons to conduct this study.
Methods:
In this study, a comprehensive questionnaire has been developed, consisting of seventy-three causes of delay. The questionnaire was organized in the form of an importance scale. Respondents were asked to indicate their responses by ticking a column of the impact and frequency of each of the causes and construction delay in terms of 5 = very important, 4 = important, 3 = somewhat important, 2 = less important, and 1 = not important. A hundred fifty questionnaires were distributed by hand to the contractor, the consultant, and the owner in the Makkah region of Saudi Arabia. Ninety-seven forms were filled, received, and processed. The survey data were grouped into eight significant categories: owner, consultant designer, supervisor, contractor, material, labor, site, and external factors. A ninth group is left for the participants to add whatever they think of furtherer causes of delay.
Results:
The evaluation of the three separate surveys conducted on the responses of the owner, the contractors, and the consultant supervisor, show that the contractor is mainly responsible for the delay. Around 47% of the top ten delay factors fall in the contractor delay factors followed by laborers and owners. Three categories have not been mentioned in the top ten as delay category, including supervisors, materials, and external factors. Only one delay factor was found to be shared among the three-survey group, which is related to the labor category, that is, low productivity of labor.
Conclusion:
Three separate surveys have been conducted to investigate the delay in the construction industry in the Makkah region of Saudi Arabia. The surveys contain a questionnaire of seventy-three possible delay factors investigating the opinions of the three main stakeholders in the construction industry: the owners, the contractors, and the consultants. The evaluation of the survey impacts shows that the contractor is mainly responsible for the delay, followed by laborers and then the owners. One common delay factor was found among the three surveyed groups related to the labor category; that is, low productivity of labor. In frequency, the contractor category also occupied the highest percentage of the total delay contributors. Another common delay factor was found among the three surveyed groups, also related to the contractor category, that being the lack of risk evaluation by the contractor.
1. INTRODUCTION
The government of Saudi Arabia has invested billions of dollars in mega projects, both super and infrastructures within the Makkah region, in the last few decades. Makkah construction projects have unique features in their magnitude and nature. Construction delay is a significant problem facing the construction industry in Saudi Arabia in general and increasingly in the Makkah region. It is widespread, and its economic and social impact is often discussed on numerous levels of authorities. The Saudi Ministry of Municipal and Rural Affairs (MOMRA) and the Ministry of Transportation acknowledged public construction project delays. They reported that about 75% of the projects exceeded their scheduled time [1].
Delays often resulting in time overrun, cost overrun, disputes, litigation, and sometimes complete abandonment of projects [2]. Delays directly impact the expected output and revenues since the contractors rely on a limited number of projects. The delays beyond the initial contract schedule cause high cost overrun to the owners in many projects, including hardship, expense, and revenue loss [3]. Many studies have investigated the causes of construction project delays in various countries. In this study, a comprehensive investigation of the causes of construction delays in the Makkah region in Saudi Arabia is conducted. The study involves the main stakeholders, the owners, the contractors, and the consultant supervisors.
1.1. Aims
This study is aiming to identify the major causes of delays in construction projects in the Makkah region of Saudi Arabia. It investigates the opinions of different stakeholders separately to ensure partiality and objectivity. The study concentrates on the reasons for regional delays rather than nationwide or globally. This would help draw a clearer picture of the delay problem facing construction projects and assist decision-makers in the building industry to draw an appropriate strategy to deal with the problem.
1.2. Background
Saudi Arabia's construction industry is experiencing rapid expansion, with no shortage of contracts in any sector, either from housing or utilities to transport infrastructure. Public spending is driving the contracting industry forward [4]. The construction industry contributed between 30% to 40% of the non-oil productive sectors at the end of each National Development Plan from 1980 to 2000 [5]. Makkah is the most populous city in Saudi Arabia, with an area of 1200 km2 and a population of 1,675,000 people. Muslims from across the globe travel to Makkah to perform the annual Hajj. Makkah receives around two million pilgrims during the annual Hajj and more than 20 million visitors for performing Umrah [6].
Substantial public funds have been spent on construction projects to develop Makkah during recent years. Real estate, infrastructure, hospitals, and retail sectors are among those most likely to benefit. Most of these projects suffered from delays and their consequences. The Saudi Ministry of Municipal and Rural Affairs (MOMRA) and the Ministry of Transportation acknowledged public construction project delays. They reported that approximately 75% of them exceeded their scheduled time. This is one of the main reasons to conduct this study. Delays often resulted in time overrun, cost overrun, disputes, litigation, and sometimes complete abandonment of projects [2]. Delays have a direct impact on the expected output and revenues as the contractors are relying on a limited number of projects.
1.3. Related Studies
Ahmed et al. [7] concluded in their study in the USA that the main reasons for the delay are; building permits approval, change of orders, changes in drawings, incomplete documents, inspections, changes in specifications, decisions during the development stage, shop drawing approval, design development and change in-laws, and regulations. Faridi and El-Sayegh [8] also conducted a study in the USA, and they concluded that the approval of drawings is the main causer of delay along with slowness of the owners, shortage of workforce, skill shortages, material shortages, building permits approval, financing by the contractor during construction and the productivity of labor.
Bromilow [9] observed that only one-eighth of the building projects in Australia were completed on time, and the averages time overrun on the projects exceeded 40%. Bordoli and Baldwin [10] found that the average time overrun of government construction projects in the UK during 1993-1994 was 23.2%. Eliis and Thomas [11], in their study on root causes of delays in highway projects in the USA, observed that time overrun in 150 projects averaged 272 days or 25% of contract duration.
Doloi et al. [12] studied the cases of delay in India. They concluded that unrealistic schedule imposed, slow decisions from the owner, unforeseen ground conditions, and delay in shop drawings approval. Low labor productivity, delay in material procurement by the contractor as the leading causes of delay.
Sambasivan and Soon [2] in Malaysia investigated ten significant causes of delays; and concluded that the most significant delays are poor management and inadequate planning. Sepasgozar et al. [13] argued that outdated construction technologies are the main factors causing the delay in construction projects.
Elinwa and Joshua [14] found that the degree of time overrun in Nigeria is between 80% and 90%. This means that only 10 to 20% of construction projects finish on schedule time. Koushki et al. [15] conducted a study of 450 private residential housing projects in Kuwait. They found that more than 56% of the projects did not complete on scheduled time, and about 44% of the projects were delayed by four months or more; one-third of the projects were delayed by more than six months.
Aibinu and Odeyinka [16] investigated the causes of delay in Nigeria. They summarized the leading causes of delay as the contractor's financial difficulties, the delay of the cash flow by the owner, incomplete drawings by the designer, slow mobilization, equipment breakdown and maintenance problems, late delivery of ordered material, and incomplete structural drawings. Mohammed and Isah [17] concluded in their study in Nigeria that improper planning, lack of effective communication, shortage of supply like steel, concrete, design factors, slow decision-making, financial issues, lack of information on design drawings, cash flow problems during construction and shortage of material are the main factors of delay.
Frimpong and Olywoye [18] studied the causes of delay in Ghana. They identified the leading causes of delay as monthly payment delays, inadequate contract management, financial difficulties by the contractors, planning and scheduling difficulties, cash flow during construction, and Inflation.
In Egypt, Abd El-Razek et al. [1] investigated the leading causes of delay in various kinds of construction projects from the point of view of different stakeholders. The overall findings indicated that the most leading causes of delay are financing the projects during construction, delays in reimbursement by the owner, the change of the initial design by owners during construction, and lack of professional management protocols. The contractor and owner were found to have conflicting views, holding each other responsible for delays, while the consultant had a more objective view. The outcome of the study indicated that teamwork is needed to minimize delays occurrence in construction projects. Furthermore, the project size is one of the parameters considered in evaluating delay analysis.
Tumi et al. [19] found that inadequate planning, financial issues, design errors, slow decision making, lack of effective communication, and supply shortage ranked the highest causer of delay in Libya.
Assaf et al. [20] conducted a study of the delay in construction projects in the Eastern province of Saudi Arabia through a questionnaire survey of contractors’ and consultants’ feedback. In their study, 76% of the contractors and 56% of the consultants specified a delay ranging between 10% to 30%, and about 25% of the consultants specified a delay of 30% to 50% of the original contract duration.
1.4. Objectives
The objective of this study is to conduct a detailed survey of all possible delay factors. The total number of these factors is seventy, classified into eight significant categories: The owner, consultant designer, supervisor, contractor, material, labor, and site. The surveys include a questionnaire on the opinions of three main stakeholders: the owners, the contractors, and the consultants. These questionnaires are to be conducted separately for each stakeholder group to ensure impartiality and objectivity. The questionnaires are to be organized in the form of an importance scale from one to five. Respondents are to indicate their responses by ticking a column of the impact and frequency of each of the causes of construction delay. The results are then processed using the Relative Importance Index. The highest-ranking factors in impact and frequency are to be identified and evaluated.
2. METHODOLOGY
In this study, a comprehensive questionnaire has been developed, consisting of seventy causes of delay. The questionnaire was organized in the form of an importance scale. Respondents were asked to indicate their responses by ticking a column of the impact and frequency of each of the causes and construction delay in terms of 5 = very important, 4 = important, 3 = somewhat important, 2 = less important, and 1 = not important. A hundred fifty questionnaires were distributed by hand to the contractor, the consultant, and the owner in the Makkah region of Saudi Arabia. Ninety-seven forms were filled, received, and processed.
150 questionnaires were distributed among stakeholders, namely, owners, contractors and consultants, both in Arabic and English. The total number of questionnaires received back was 114, and the details are presented in Table 1.
| Recipient | Dispatched | Collected |
|---|---|---|
| Owner | 50 | 42 |
| Contractor | 50 | 36 (11 subcontractors, 25 contractor) |
| Consultant | 50 | 36 (19 supervisors, 17 designers) |
| Total | 150 | 114 |
The participants were mainly government projects that constitute 95% of the projects that participated in the survey. The delay problem is more prominent in the governmental sector, which explains the high percentage of government sector responses (Table 2).
| Sector/ownership | Contractor | Consultant Designer/Supervisor | Owner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government | 36 | 42 | 36 |
| Private | 0 | 0 | 6 |
The questionnaire contains a variety of job descriptions of the participants. Their numbers and affiliations are tabulated in Table 3.
| Job Description | Contractor | Consultant Designer/Supervisor | Owner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Owner | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Project/Construction manager | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Site Engineer | 18 | 20 | 25 |
| Safety Engineer | 5 | 2 | 4 |
| Quality Control Eng. | 10 | 6 | 8 |
| Supplier | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Various types of construction projects participate as can be seen in Table 4.
The questionnaire investigated the experience of participants measured by years, as seen in Table 5.
| Industry type | Contractor | Consultant Designer/Supervisor | Owner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superstructure | 21 | 21 | 28 |
| Infrastructure | 8 | 15 | 7 |
| Oil & Gas | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Retrofitting/rehabilitation | 7 | 0 | 7 |
| Total experience in construction in Years | Contractor | Consultant Designer/Supervisor | Owner |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 to 5 | 9 | 7 | 16 |
| 6 to 10 | 17 | 19 | 12 |
| 11 to 15 | 7 | 7 | 10 |
| 16+ | 3 | 3 | 4 |
Various sizes of companies were investigated, as seen in Table 6.
| Size of your company or organization | Contractor | Consultant Designer/Supervisor | Owner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large (>250 employees) | 0 | 16 | 38 |
| Medium (50 < employees < 250) | 3 | 15 | 4 |
| Small (10 < employees < 50) | 18 | 4 | 0 |
| Micro (< 10 employees) | 5 | 1 | 0 |
The survey data were grouped into eight significant categories: owner, consultant designer, supervisor, contractor, material, labor, site, and external factors. A ninth group is left for the participants to add whatever they think of furtherer causes of delay. The categories and various causes of delays are shown in Tables 7-14.
| S/N | Delay Factor | Delay Category |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Delay in decision-making commensurate with the agreement of the parties to the project. | Owner |
| 2 | Suspension of work. | |
| 3 | Delay in revising and approving documents by the owner. | |
| 4 | Delay in delivering construction site to the contractor. | |
| 5 | Delay of financing and payments by the owner. | |
| 6 | Delay due to changes in the project description by the owner. | |
| 7 | Re-tendering due to over budget. | |
| 8 | Unrealistic enforced contract duration. | |
| 9 | Delay by owner in handing over process or approval of completed work. | |
| 10 | Delay due to unsolved wright of away. | |
| 11 | Delays in performance due to unclear coordinate of underground utility. | |
| 12 | Lack of experience of the owner in the approval of the supervision team. |
| S/N | Delay Factor | Delay Category |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lack of supervisor consultant experience and wrong approval. | Consultant supervisor |
| 2 | Delay in approval of submittals, design drawings, shop drawings, and sample materials. | |
| 3 | Delay due to mistakes or discrepancies in documents or specifications. | |
| 4 | Lack of communication and coordination with other project parties. | |
| 5 | Negligence of finishing the work according to the initial schedule. |
| S/N | Delay Factor | Delay Category |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lack of design team experience and frequent design errors. | Designer |
| 2 | Errors in calculating the initial project time by the designer. | |
| 3 | The designer does not comply with the code of design. | |
| 4 | The absence of the designer while modifying the design or correcting the wrong designs. | |
| 5 | The designers' incompatibility to change the design with the rest of the project parties. | |
| 6 | Incompatibility of parties with different disciplines. |
| S/N | Delay Factor | Delay Category |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Difficulties in financing the project. | Contractor |
| 2 | Delay due to inadequate site management and improper task distribution. | |
| 3 | Delay due to improper estimate of task duration. | |
| 4 | Rework due to errors during construction. | |
| 5 | Delays related to works performed by sub-contractors. | |
| 6 | Lack of experience of the contractor (Poor qualification of the contractors' staff). | |
| 7 | Inappropriate construction methods. | |
| 8 | Poor communication and coordination with other parties. | |
| 9 | Unsafe practice at the site (Poor safety conditions and application of safety regulations on-site). | |
| 10 | Inadequate equipment on site. | |
| 11 | Lack of technical skills of the project manager. | |
| 12 | Lack of managerial skills of the project manager. | |
| 13 | Lack of risk evaluation. | |
| 14 | Lack of evaluation increases and decreases in the schedule during the execution of the project. | |
| 15 | Deficiency in planning and scheduling the project. | |
| 16 | The size of the work is more than the resources owned by the contractor. | |
| 17 | Lack of training and adopting a new technique. | |
| 18 | Lack of support from the executive management. | |
| 19 | Delay when the contractor ignores the work sequence suggested by the supervisor and the owner. |
| S/N | Delay Factor | Delay Category |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rejection of materials by the owner if it does not meet specifications requirements. | Materials |
| 2 | Lack of material close the site. | |
| 3 | Delays due to material delivery. | |
| 4 | Changes in material type and specifications during construction. | |
| 5 | Delay due to Inflation and escalation of material prices. |
| S/N | Delay Factor |
|---|---|
| 1 | Delay due to late start leads to a late finish. |
| 2 | Inadequate crew size. |
| 3 | Low productivity of labor. |
| 4 | Strike. |
| 5 | Lack of motivation. |
| 6 | Late salary and compensation. |
| 7 | Workers used for more extended hours. |
The relative importance index has been used to identify the importance of the impact of each cause of delay along with the frequency of that cause. The relative importance index (RII) was calculated using the following formula [21, 22]:
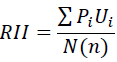 |
Where,
RII = relative importance index
Pi = respondents rating of the cause of delay
Ui = number of respondents placing identical weighting/rating on the cause of delay
N = sample size
n = the highest attainable score on the cause of delay
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1. Owners Response
Table 15 shows the top ten delay RII impact factors globally found from the owner’s response. All the ten RII for the impact are high. This indicates the high effect of these factors. None of the ten delay factors are related to the owner. This may cast doubt on this evaluation. Therefore, these findings need to be verified by considering the responses of other stakeholders. The top three factors in their impacts are found to be (1) low productivity of labor (RII = 0.92), (2) lack of evaluation in increase and decrease in the schedule periodically (RII = 0.88), (3) late start and early finish (RII = 0.88). The first and second are related to the labor group, and the third is related to the contractor group.
Table 16 shows the highest ten delay RII factors related to frequencies out of seventy delay factors from the owner perspective. Only one out of ten is attributed to the owners. The highest three in frequency RII are (1) Late start and early finish (RII = 0.83), (2) Late salary and compensation (RII = 0.82), (3) Size of work is more than the resources owned by the contractor (RII = 0.8). Although it is common in project delays that blame is put on the sub-contractors, the ultimate responsibility is on the main contractor according to the regulations of Saudi contracts.
| S/N | Delay Factor | Delay Category |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lack of equipment or maintenance. | Construction site |
| 2 | Unforeseen site conditions such as:(Unexpected subsurface conditions, soil problems, and high-water table. | |
| 3 | An inappropriate number of equipment or incompatibility between them. | |
| 4 | Restriction at the job site (Poor site access, traffic congestion, and security). | |
| 5 | Lack of site utilities or services such as (water, electricity, and sewer). | |
| 6 | An accident during construction. | |
| 7 | Problem with nearby structures or facilities (Disturbance to public activities, the effect of social, and cultural factors). | |
| 8 | Hazardous substance. | |
| 9 | Difficulties on the project site. | |
| 10 | Delay due to security and restrictions. |
| S/N | Delay Factor | Delay Category |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Weather factor (heat, flood, etc.). | External factors |
| 2 | Delay due to the change in government regulations and laws. | |
| 3 | Delay in inspection and issuing the approval by consultant or indecent laboratory according to specifications. | |
| 4 | Global financial crisis | |
| 5 | Force Majeure (earthquake, flood, and other natural disasters). | |
| 6 | Delay due to procedure of dispute between stakeholders. |
| Rank | Delay Factors | Category | RII |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Low productivity of labor | Labor | 0.92 |
| 2 | Lack of evaluation increases and decreases in the schedule during the execution of the project. | Contractor | 0.88 |
| 3 | The late start and early finish | Labor | 0.88 |
| 4 | Delay of financing and payments by the owner | owner | 0.86 |
| 5 | Delay due to inadequate site management and improper task distribution. | Contractor | 0.85 |
| 6 | The size of work is more than the resources owned by the contractor | Contractor | 0.85 |
| 7 | Lack of training and adopting a new technique | Contractor | 0.85 |
| 8 | Delays due unclear coordinate of underground utility | owner | 0.84 |
| 9 | Delays related to sub-contractor’s work. | Contractor | 0.84 |
| 10 | Lack of experience of a contractor (Poor qualification of contractor’s staff) | Contractor | 0.84 |
| Rank | Delay Factors | Category | RII |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Late start and early finish | Labor | 0.83 |
| 2 | Late salary and compensation | Labor | 0.82 |
| 3 | The size of work is more than the resources owned by the contractor | Contractor | 0.8 |
| 4 | Lack of risk evaluation | Contractor | 0.8 |
| 5 | Deficiency in planning and scheduling the project. | Contractor | 0.8 |
| 6 | Difficulties in financing the project | Contractor | 0.8 |
| 7 | Lack of evaluation increases and decreases in the schedule during the execution of the project. | Contractor | 0.79 |
| 8 | Delays due unclear coordinate of underground utility | owner | 0.79 |
| 9 | Ignoring the sequence suggested by the supervisor and the owner | Contractor | 0.79 |
| 10 | Lack of training and adopting a new technique | Contractor | 0.78 |
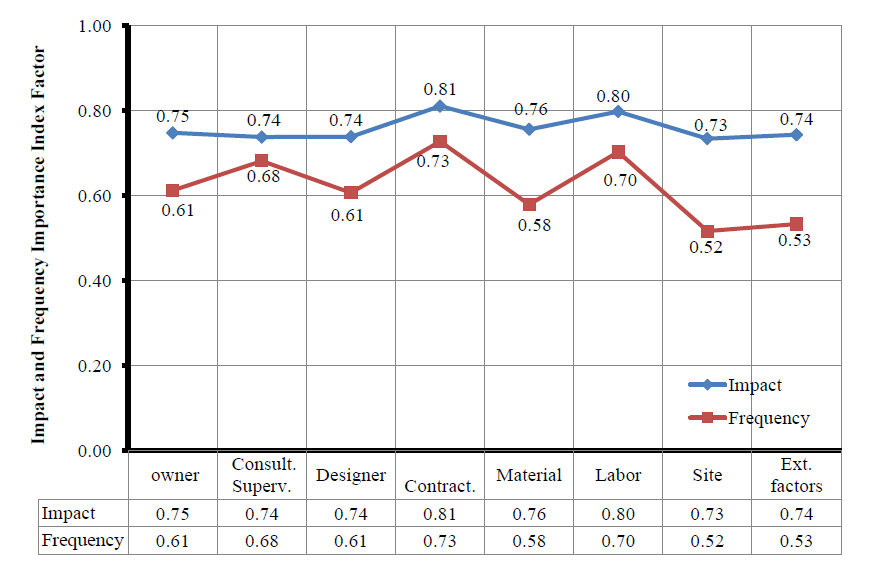
Fig. (1) shows the average RII for the impact and frequency of the eight categories. The contractor is the main influential factor in project delays from the owner's point of view, both in impact and frequency.
Labor comes second with relatively close values to the contactor values. Materials come third in impact but low in frequency, indicating low occurrence and thus fewer delay occurrences. In the overall average of the impact index of all groups, the highest was the delays caused by the contractor group, followed by delays caused by labor, and finally delays related to consultant supervisor groups. The overall average of the frequency index of all groups seems to be relatively low. However, the highest rank of frequency index is related to delays caused by the contractors, followed by labor, and thirdly by the consultant supervisor. The objectivity of these results needs to be compared and verified with the results obtained from the rest of the stakeholders who participated in the surveys.
3.2. Contractors Response
Table 17 shows the top ten delay RII impact factors globally found from the contractor response. All the ten RII for the impact are high. This indicates the high effect of these factors. None of the ten delay factors are related to the contractor. This may cast doubt on this evaluation. Therefore, these findings need to be verified by considering the responses of other stakeholders. The top three factors in their impacts are found to be (1) delay in decision-making commensurate with the agreement of the parties to the project (RII = 0.89), (2) unqualified and unskilled workforce (RII = 0.87), (3) low productivity of labor (RII = 0.87). The first is related to the owner group, second and third are related to the labor group. It is evident from Table 11 that all the top ten delay factors RII values are very close to each other and range between 0.86 and 0.89.
| Rank | Delay Factors | Category | RII |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Delay in decision-making commensurate with the agreement of the parties to the project | Owner | 0.89 |
| 2 | Unqualified and unskilled workforce | Labor | 0.87 |
| 3 | Low productivity of labor | Labor | 0.87 |
| 4 | Hazardous substance | site | 0.87 |
| 5 | Suspension of work | Owner | 0.86 |
| 6 | Delay due to changes in the project description by the owner. | Owner | 0.86 |
| 7 | Unrealistic enforced contract duration | Owner | 0.86 |
| 8 | Delay in approval of submittals, design drawings, shop drawings, and sample materials. | Consultant supervisor | 0.86 |
| 9 | Lack of design team experience and frequent design errors | Designer | 0.86 |
| 10 | Late salary and compensation | Labor | 0.86 |
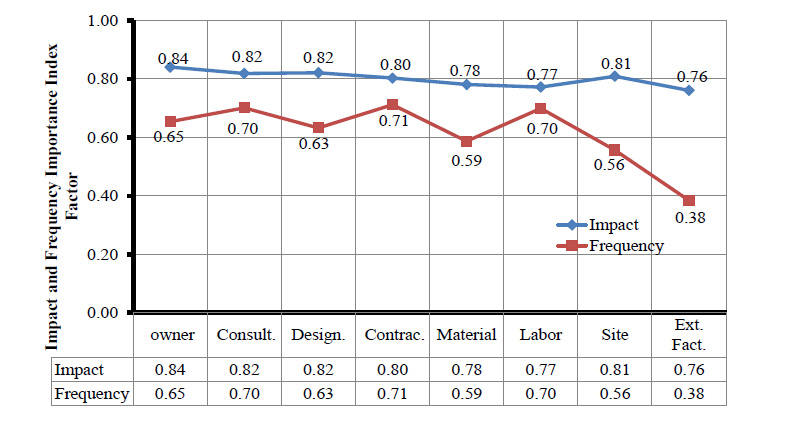
Table 18 shows the highest ten delay RII factors related to frequencies out of seventy delay factors from the contractor’s perspective. Five out of ten are attributed to the contractor, including the top two. These findings seem to be reliable because they contain self-admission by the contractors. The highest three in frequency RII are (1) delays related to subcontractors' works (RII = 0.84), (2) poor management of the site and lack of distribution of tasks (RII = 0.82), (3) workers used for more extended hours (RII = 0.81). Although it is common in project delays that blame is put on the sub-contractors, the ultimate responsibility is on the main contractor according to the regulation of Saudi contracts (Fig. 2).
| Rank | Delay Factors | Category | RII |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Delays related to works performed by sub-contractors. | Contractor | 0.84 |
| 2 | Delay due to improper estimate of task duration. | Contractor | 0.82 |
| 3 | Workers used for more extended hours. | Labor | 0.81 |
| 4 | Delay in approval of submittals, design drawings, shop drawings, and sample materials. | Consultant supervisor | 0.79 |
| 5 | Late salary and compensation. | Labor | 0.79 |
| 6 | Lack of risk evaluation. | Contractor | 0.79 |
| 7 | Delay in decision-making commensurate with the agreement of the parties to the project | owner | 0.78 |
| 8 | Inappropriate number of equipment or incompatibility between them. | site | 0.78 |
| 9 | Deficiency in planning and scheduling the project. | Contractor | 0.78 |
| 10 | Lack of managerial skills of project manager | Contractor | 0.78 |
3.3. Consultants Supervisors Response
Table 19 shows the top ten delay factors globally found from the responses from the consultant supervisors. All the ten RII for the impact are high. This indicates the high effect of these factors. Eight out of ten of them are related to the contractor. This may cast doubt on this evaluation. Therefore, these findings need to be verified by considering the responses of other stakeholders. The top three factors in their impacts are found to be (1) difficulties in financing the projects (RII = 0.91), (2) poor site management, and lack of distribution of tasks (RII = 0.89), (3) low productivity of labor (RII = 0.86). The first two are delay factors related to the contractor group, and the third is related to the labor group.
Table 20 shows the highest ten delay RII factors related to frequencies out of seventy delay factors from the consultant supervisor perspective. Nine out of ten are attributed to the contractor. The highest three in frequency RII are (1) delays related to sub-contractor work (RII = 0.74), (2) Poor estimate of task duration and scheduling (RII = 0.72), (3) Lack of risk evaluation (RII = 0.72). These findings need to be compared with the responses of other stakeholders to evaluate the validity of one opinion.
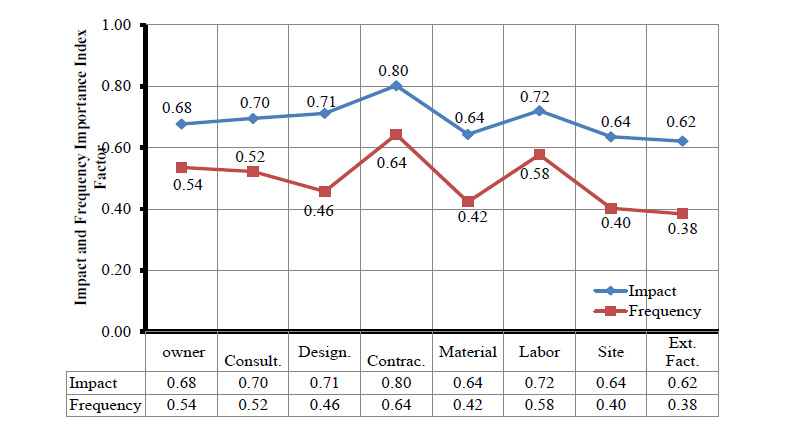
Fig. (3) shows the overall average impact and frequency of the eight categories, namely, owner, consultant supervisor, designer, contractor, labor, material, site, and external factors. In the overall average impact index, the highest was the delays due to the contractor group, followed by delays due to labor, and thirdly, delays related to the designer category.
The overall average of the frequency index of most groups seems relatively low. The highest was attributed to the contractor, the second to the labor, and the third to the owner. The outcome of this analysis is based on the consultant's opinion; therefore, the objectivity of these findings needs to be compared and verified with the results obtained from the survey of other stakeholders.
| Rank | Delay Factors | Category | RII |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Difficulties in financing the project. | Contractor | 0.91 |
| 2 | Delay due to inadequate site management and improper task distribution. | Contractor | 0.89 |
| 3 | Low productivity of labor | Labor | 0.86 |
| 4 | Deficiency in planning and scheduling the project. | Contractor | 0.85 |
| 5 | Lack of risk evaluation | Contractor | 0.84 |
| 6 | Delay in approval of submittals, design drawings, shop drawings, and sample materials. | Consultant supervisor | 0.83 |
| 7 | Inadequate Equipment on site. | Contractor | 0.83 |
| 8 | Lack of managerial skills of the project manager. | Contractor | 0.83 |
| 9 | Delays related to works performed by sub-contractors. | Contractor | 0.82 |
| 10 | Unsafe practice at the site (Poor safety conditions and lack of application of safety regulations on-site). | Contractor | 0.81 |
| Rank | Delay Factors | RII | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Delays related to works performed by sub-contractors. | 0.74 | Contractor |
| 2 | Delay due to improper estimate of task duration. | 0.72 | Contractor |
| 3 | Lack of risk evaluation | 0.72 | Contractor |
| 4 | Delay due to inadequate site management and improper task distribution. | 0.71 | Contractor |
| 5 | Lack of risk evaluation | 0.71 | Contractor |
| 6 | Lack of training and adopting a new technique | 0.69 | Contractor |
| 7 | Inadequate crew size | 0.69 | Labor |
| 8 | Lack of managerial skills of project manager | 0.68 | Contractor |
| 9 | Difficulties in financing the project | 0.67 | Contractor |
| 10 | Deficiency in planning and scheduling the project. | 0.67 | Contractor |
3.4. Findings
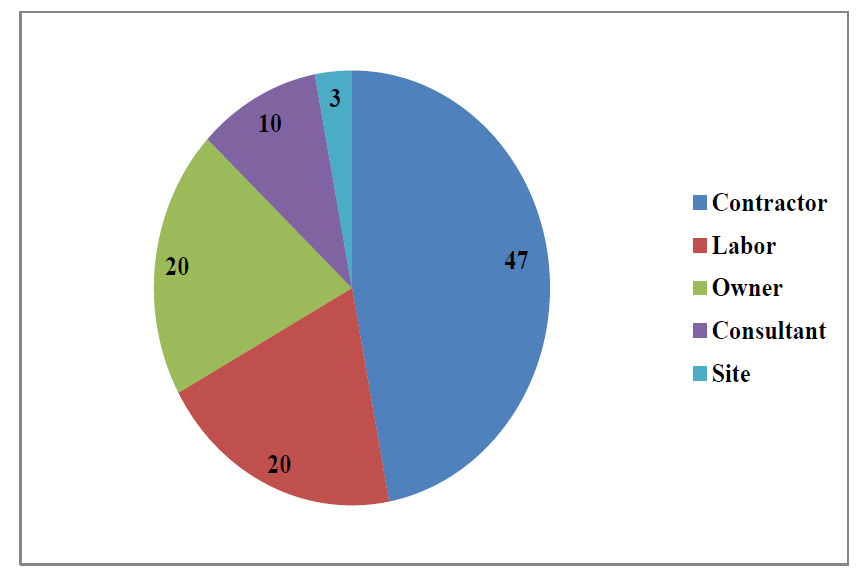
The evaluation of the three separate surveys conducted on the owner, the contractors, and the consultant supervisor shows that the contractor is mainly responsible for the delay. Around 47% of the top ten delay factors fall in the contractor delay factors followed by laborers and owners. Fig. (4) summarizes the percentage of the delay categories. Three categories have not been mentioned in the top ten as delay category, including supervisors, materials, and external factors. Only one delay factor was found to be shared among the three-survey group, which is related to the labor category, that is, low productivity of labor.
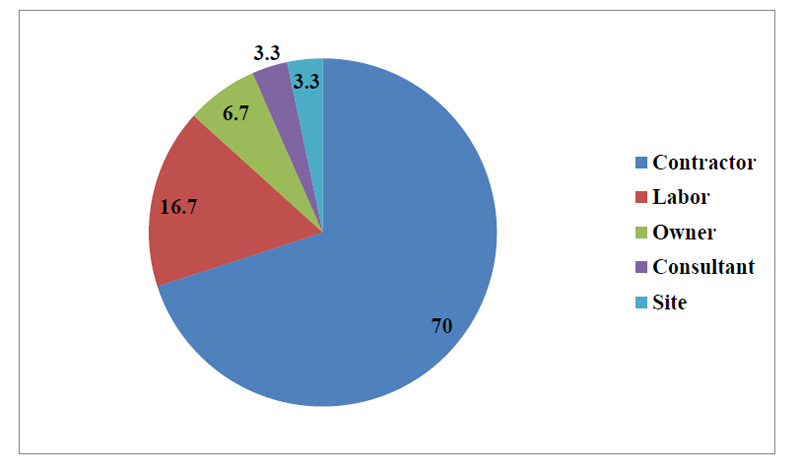
Also, in frequency, the contractor category occupied the highest percentage with 70% of the total contributors. This and the rest of the delay contribution in the frequency of each category are presented in Fig. (5). Only one delay factor was found to be shared among the three survey groups, which are related to the contractor category, that is, the lack of risk evaluation by the contractor.
CONCLUSION
Three separate surveys have been conducted to investigate the delay in the construction industry in the Makkah region of Saudi Arabia. The surveys contain a questionnaire of seventy possible delay factors investigating the opinions of the three main stakeholders in the construction industry: the owners, the contractors, and the consultants. The evaluation of the survey impacts shows that the contractor is mainly responsible for the delay, followed by laborers and then the owners. One common delay factor was found among the three surveyed groups related to the labor category; that is, low productivity of labor. In frequency, the contractor category also occupied the highest percentage of the total delay contributors. Another common delay factor was found among the three surveyed groups, also related to the contractor category, that being the lack of risk evaluation by the contractor.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
Not applicable.
FUNDING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Declared none.


